Cardiovascular imaging
IMPC cluster of excellence

Maladie cardiovasculaire
The cardiovascular center's medical staff
The division cardiovascular imaging IMPC is one of the region's leading cardiovascular imaging divisions. The division's medical staff is made up of radiologists specializing in the cardiovascular field. Indeed, this medical corps possesses a wide range of expertise in the cardiac and vascular diagnosis of adult and pediatric patients. The members of our cardiovascular center are national leaders in the field of cardiovascular imaging and cardiovascular imaging research.
Availability of advanced cardiovascular imaging techniques
Thecardiovascular imaging performs state-of-the-art diagnostic evaluations using the latest generation of imaging technologies. computer tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and molecular imaging. Our extensive facilities include outpatient, inpatient and specialized research facilities on the main campus and at several other sites in the Paris region. Each of these facilities is supported by a team of expert physicists, nurses and technologists.
What is a coronary CT scan?
A coroscanner also known as a "coronary artery scanner", is a medical imaging test that explores your arteries. heartthe coronary arteriesin search of possible lesions (stenosis, occlusion ...). In certain cases, this examination is particularly crucial.
Why have a coronary artery scan?
In the case of atypical chest pain, the coroscanner is particularly recommended. In fact, it consists in searching for coronary calcifications to detect a high risk of coronary problems in patients.
What's more, a CT scan can help guide treatment if you have a low risk of heart disease or if your risk of heart disease is unclear.
Finally, a coroscanner can also help people at moderate risk to make important lifestyle changes and follow treatment plans. However, it is an essential tool for detecting certain abnormalities.
What anomalies can be detected by a coroscanner?
Coroscanner is particularly useful for :
- The study of coronary arteries
- Study of calcified and/or soft plaques and degree of stenosis
- Post-operative control of aorto-coronary bypass surgery and stents
- Pre-surgical assessment of valvulopathy
- The detection of stenoses coronary arteries (atypical chest pain)
- These congenital heart disease : birth defect of the coronary arteries
This examination requires special preparation. Don't worry, our health professionals will always be there to support you!
How does a coronary CT scan work?
A heart being a mobile organ, the arteries are visualized at a precise moment in the cardiac cycle. The scanner must be coupled to theelectrocardiogram and your heart rate should be slow, around 60/minute. It may be necessary to inject medication and wait a while before achieving a slow enough heart rate. The injection of an iodinated contrast medium is essential to opacify the coronary arteries.
When the contrast medium is injected, the patient must remain motionless and observe an apnea of around 15 seconds. A calcium score is taken first.
How can a coroscanner help reduce cardiac risk?
One of the reduce risk is to detect these conditions early, and to treat and manage patients appropriately. Your doctor will use the results of your test to determine what you need - medication or lifestyle changes - to reduce your risk of heart attack or other heart problems.
All in all, if the need arises, the coroscanner offers undeniable advantages.
What are cardiovascular imaging tests?
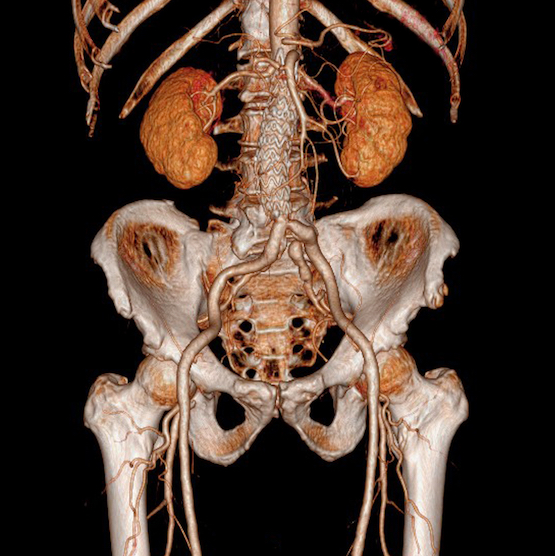
ANGIOSCANNER
ARTERIOVENOUS DOPPLER
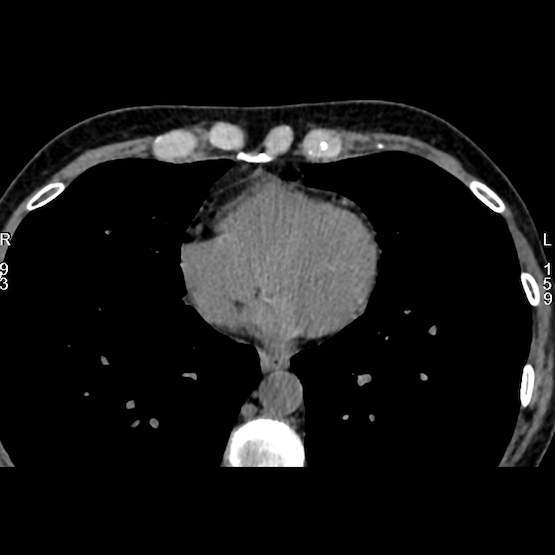
CALCULAR SCORE
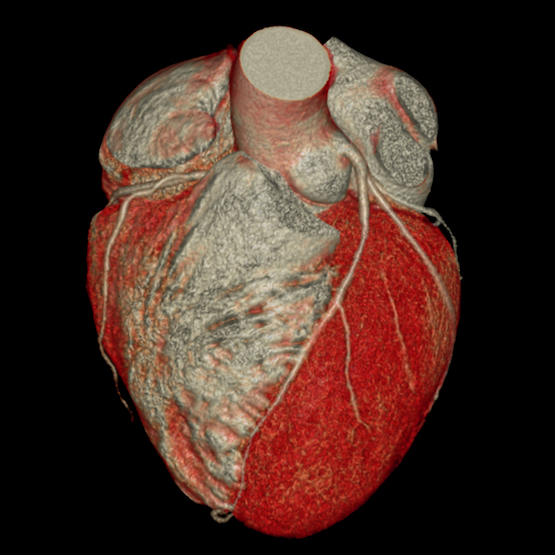
COROSCANNER
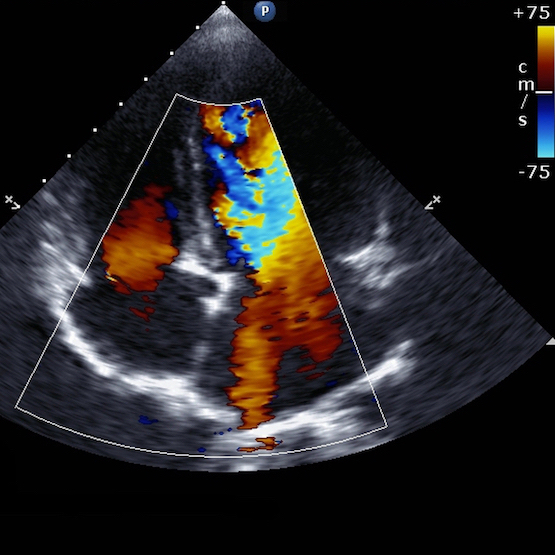
Cardiovascular Doppler
Doppler is an ultrasound technique used to analyze blood flow and vessel walls.
Venous Doppler is indicated for exploring venous pathologies of the limbs. In the event of acute pain and swelling, it can be used to detect acute vein thrombosis (phlebitis).
Venous Doppler is also used to map chronic venous disease of the lower limb, to search for signs of venous insufficiency and varicose veins. The technique can also be used to guide sclerotherapy in the treatment of varicose vein disease.
Calcium score
Calcium score imaging, performed by coronary CT, is a diagnostic method for assessing the risk of cardiovascular disease by measuring the amount of calcium present in the coronary arteries. This examination provides crucial information on heart health by identifying the calcification of atherosclerotic plaques, an indicator of atherosclerosis.
During this examination, the patient is positioned on a CT table, and a scanner produces detailed images of the heart. The calcium score is calculated according to the density of calcium in the arteries, measured in Hounsfield units (HU). A higher score indicates increased calcification and, consequently, a higher risk of heart disease.
This type of imaging detects the presence of calcified plaques, precursors of atherosclerosis, and provides an estimate of the overall risk of coronary heart disease. The results, expressed as a score, are interpreted according to specific ranges, enabling doctors to identify patients at risk and adapt treatment and prevention strategies accordingly.
Although the calcium score is a powerful indicator of cardiovascular risk, it is important to note that calcification does not always reflect the presence of significant arterial stenosis. Some patients may present calcified plaques without major arterial obstruction.
